The biggest crisis of modern times…Being an unprecedented pandemic throughout the past century, Covid-19 has changed people’s lives completely. Many governments took strict measures to prevent the spread of the virus and a collapse in healthcare systems. While the potential customers practice social distancing at their homes, serious issues started to arise among nonessential businesses being ordered to close. Many had to close down for an undetermined period, not just because of social distancing but also because of curfews. And there was a considerable demand for shopping—especially for disposable sanitary products. Still, traditional retailing had its rough edges: face-to-face buying and selling, definitely more physical contact than needed, quite little elbow room. However, the widespread use of the internet and advanced technology let businesses reach their audience despite social distancing. Not surprisingly, e-commerce has started to grow more than any time in its history.
How E-Commerce Got Affected by Covid-19?
The strong and steady growth of internet users and increased awareness of online shopping increased the online launch of goods, and low prices due to bulk sales are the factors that drive the growth of the e-commerce industry before the Covid-19 pandemic. Besides, the growing number of exclusive items on the market and the lower prices of goods further support global e-commerce. Moreover, after the COVID-19 pandemic, social distancing and remaining at home are expected to drive customers towards online shopping.

Covid-19 might have obliged business owners to switch to digital, but digital transformation undoubtedly served them well. The crisis has expanded the scope of e-commerce by easing starting a new business, adding new customer profiles such as elders, and new products like groceries. According to the report of UNCTAD issued in October 2020, the majority of participants from emerging economies like Turkey, China, and the Republic of Korea stated that they have been shopping online more often since the Covid-19 outbreak. Differently, much fewer consumers from developed economies shared that they have increased their online purchasing activities. A slightly substantial increase in e-commerce customer numbers might be expected in the developing countries for the upcoming years.

Across all the e-commerce sectors, the most considerable growth due to Covid-19 breakout belongs to gardening&do-it-yourself products, pharma&healthcare products, and consumer electronics by 9 percent, 9 percent, and 10 percent, respectively. During the pandemic, cosmetic&personal care, digital entertainment, and food&beverages are the categories with the most active users. Moreover, consumers from developing countries are more likely to shop more online in the post-Covid-19 future. Also, an increase in the use of the internet to search for health-related information is expected in the same countries.

Consumers from China and Turkey are expected to continue buying online more than physical stores in future purchasing channels. In contrast, customers from Germany, Italy, Switzerland, and Russia anticipate exhibiting a more balanced behavior between online and traditional shopping.
What are The Challenges Faced In E-Commerce During Covid-19?
Some of these changes in the e-commerce area are likely to be of a long-term nature, given the potential for new waves of the pandemic, the comfort, and the accessibility of new buying habits. However, there are still some obstacles to be removed. Despite some governments’ efforts to foster the development of e-commerce during the pandemic, regulations that are not adaptable for e-commerce are posing a problem for new firms. Also, persistent gaps in terms of e-commerce participation remain for small and medium enterprises. According to the OECD report, the participation rate for small and medium enterprises in e-commerce in 2017 was less than half the rate for large firms in most OECD countries. Low levels of digitalization and challenges in accessing and implementing new technologies make it especially difficult for these companies to modify current work processes by introducing a teleworking or e-commerce distribution platform. Although many of these issues existed before the pandemic, the current crisis and the new position of e-commerce for customers and firms have raised the importance of implementing new policies.
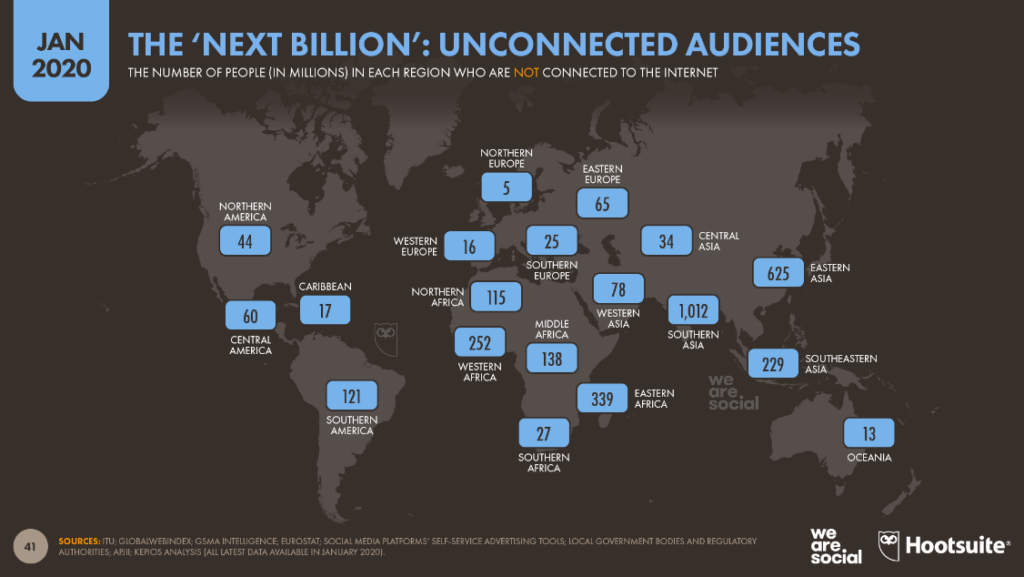
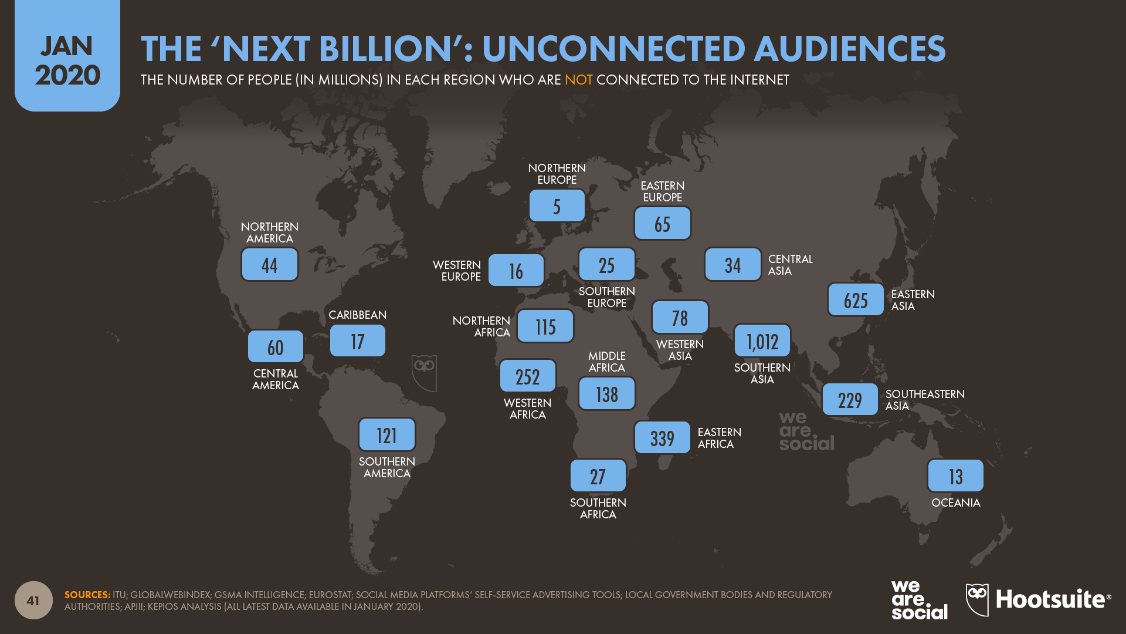
As for customers, problems related to connectivity, financial inclusion, and trust are the main challenges. According to the latest numbers, roughly 3.2 billion people remain unconnected to the internet. This makes up almost 30 percent of our population. To resolve this problem, governments should expand affordable and quality broadband to rural and underserved areas. Trust is another trouble for customers. E-commerce sites should have security certificates, trust seals, and privacy policies to ensure that their data is safe.
Governments and policymakers should support creative business models by adopting new regulations that apply to online and offline commerce channels. Small and medium enterprises should also be given a more fair field in terms of intermediated services—online platforms in this case. Competition should be sufficient enough, including improved communication services, logistics, and trade.
How is Cybersecurity Affected by Widespread E-Commerce?
The growth in e-commerce has carried with countless cybersecurity problems such as phishing attacks and web skimming. According to Imperva’s report, e-retailers have experienced more than twice as many account takeover attempts than other industries this year. Almost 79% of retailers suffered credential stuffing, where previously breached credentials are used in automated attacks across large numbers of sites. And the exposure in March 2020 to compromised e-commerce websites is higher than ever – a 26 percent rise in web skimming. In web skimming, hackers may penetrate customers’ login data and their banking details by stealing their information through mobile numbers or email addresses. However, cybersecurity professionals react urgently to increased cyber threats, and their responses cover the range of capabilities for data security and privacy management.
To reduce the risk of cyber attacks, the customers’ credit card data mustn’t be stored, and websites should obtain PCI DSS accreditation. Moreover, to secure transactions on the site, SSL certificates are crucial. The certificates are also proof of ownership of the site and a way of preventing counterfeit for phishing. Antivirus and antimalware software are another option to consider. This software provides a fraud risk score to check the legitimacy of any transaction on the site.
After the Covid-19 outbreak, with confinement measures being an obligation, online shopping has gained enormous importance. With the increase in online shopping numbers, an unexpected problem emerged: cyber attacks like web skimming. Now, cybersecurity is more important than ever. Thus, companies should allocate more resources to cyber safety specialists to protect their data and customer base.
References
S. Mandal and D. A. Khan, “A Study of Security Threats in Cloud: Passive Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic,” 2020 International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Trichy, India, 2020, pp. 837-842, doi: 10.1109/ICOSEC49089.2020.9215374.
https://unctad.org/system/files/official-document/dtlstictinf2020d1_en.pdf
https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2020-global-digital-overview
https://www.stackline.com/news/top-100-gaining-top-100-declining-e-commerce-categories-march-2020